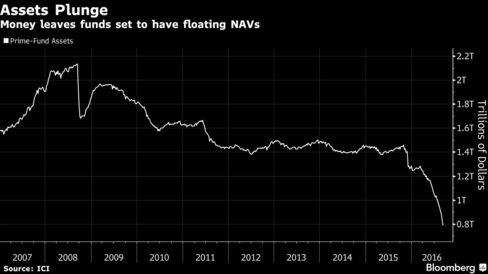
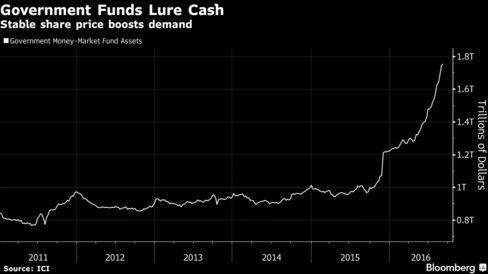
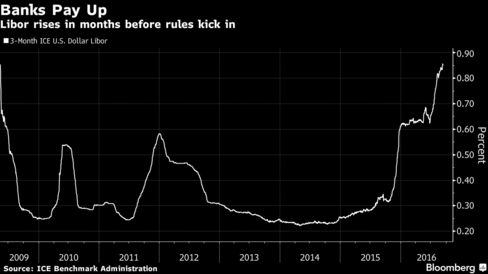
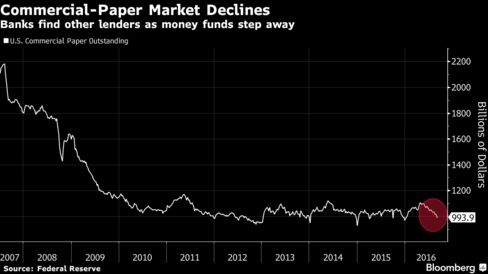
Oscar winners, sports stars and Bill Gates are building lavish bunkers — with amenities ranging from a swimming pool to a bowling alley — as global anxiety fuels sales and owners "could be the next Adam and Eve."
Given the increased frequency of terrorist bombings and mass shootings and an under-lying sense of havoc fed by divisive election politics, it's no surprise that home security is going over the top and hitting luxurious new heights. Or, rather, new lows, as the average depth of a new breed of safe haven that occupies thousands of square feet is 10 feet under or more. Those who can afford to pull out all the stops for so-called self-preservation are doing so — in a fashion that goes way beyond the submerged corrugated metal units adopted by reality show "preppers" — to prepare for anything from nuclear bombings to drastic climate-change events. Gary Lynch, GM at Rising S Bunkers, a Texas-based company that specializes in underground bunkers and services scores of Los Angeles residences, says that sales at the most upscale end of the market — mainly to actors, pro athletes and politicians (who require signed NDAs) — have increased 700 percent this year compared with 2015, and overall sales have risen 150 percent. "Any time there is a turbulent political landscape, we see a spike in our sales. Given this election is as turbulent as it is, we are gearing up for an even bigger spike," says marketing director Brad Roberson of sales of bunkers that start at $39,000 and can run $8.35 million or more (FYI, a 12-stall horse shelter is $98,500).
Adds Mike Peters, owner of Utah-based Ultimate Bunker, which builds high-end versions in California, Texas and Minnesota: "People are going for luxury [to] live underground because they see the future is going to be rough. Everyone I've talked to thinks we are doomed, no matter who is elected." Robert Vicino, founder of Del Mar, Calif.-based Vivos, which constructs upscale community bunkers in Indiana (he believes coastal flooding scenarios preclude bunkers being safely built west of the Rockies), says, "Bill Gates has huge shelters under every one of his homes, in Rancho Santa Fe and Washington. His head of security visited with us a couple years ago, and for these multibillionaires, a few million is nothing. It's really just the newest form of insurance."

A hidden door by Creative Home Engineering leads to a secret passageway that connects to an underground bunker.
Rising S Bunkers installed a 37-room, 9,000-square-foot complex in Napa Valley for an Academy Award-winning client that rang in at $10.28 million, with a bowling alley, sauna, jacuzzi, shooting range and an ultra-large home theater. Swimming pools, greenhouses, game rooms and gyms are other amenities offered. This year, on another Napa Valley property, the company constructed a $9 million, 7,600-square-foot compound with horse stables and accommodations for 12, along with four escape tunnels leading to outlets on the estate, multiple hidden rooms — in case "you let someone in whom you do not fully trust," says Lynch — and an aboveground safe house "disguised as a horse barn." The company also is designing a $3 million bunker for "a major sports figure from Southern California."
The company's best-selling bunkers for L.A. are 10 by 50 feet, start at $112,000 and have their own power sources, water supplies and air-filtration systems: "These complexes accommodate families of four or five and are self-sustaining," says Roberson, adding: "You can pretty much put a palace underground anywhere there is physically enough room." Regardless, Ellia Thompson, chair of land use practice at Ervin Cohen & Jessup in Beverly Hills, notes that zoning guidelines vary throughout L.A., so one should check with the city department of building and safety about permits: "A special permit may be required if you are digging out more dirt than certain basement quantities."
Business has doubled in the past year at Ultimate Bunker, which just built a $10 million complex on a 700-acre property a few hours north of Minneapolis for a client "known for television, who has his own show," says Peters. Two 1,000-square-foot bunkers (one for storage) are connected by 300 feet of tunnels to the main 6,800-square-foot home as well as three guesthouses that each boast a $200,000 bunker "to take care of his family and friends," says Peters. "It's like an underground mansion with more mansions on top of it."
Al Corbi, president and founder of S.A.F.E. (Strategically Armored & Fortified Environments), with offices in West Hollywood, says that his most spectacular projects were $100 million subterranean residences, one for a global venture capitalist and the other for an East Coast developer to mimic the Universal CityWalk promenade, with a pizzeria and wellness outpost that, he says, "resembles a Burke Williams day spa." Corbi says both bunkers protect from nuclear holocaust (8 feet of soil blocks radioactive fallout), pandemic (a positive-pressure air system with HEPA filters keeps contaminants out), electromagnetic pulses and solar flares (using a metal encasement), among other threats. "Power technology has improved tremendously thanks in part to Tesla and lithium-ion batteries that only degrade a maximum of 10 percent after 30 years," says Corbi. "And now there is food with a 25-year minimum shelf life. [The owners] could be the next Adam and Eve." (Note to L.A. chefs, however: The rations are grim, ranging from beef Stroganoff to chili.)
When it comes to the details of secret passageways and hidden doors, many in Hollywood turn to Arizona-based Creative Home Engineering. "We've seen year-over-year growth of about 20 percent, but perhaps more telling is an increasing percentage of clientele who need their secret door to employ high-security features," notes president Steve Humble, who says before, 60 percent of secret doors in cigar rooms, home theaters, children's bedrooms and the like were for novelty value. "Nowadays, 80 percent are used for security. In the past year, I have performed installations inside two nuclear-protected complexes with more than 10 secret doors each, one in the L.A. area owned by a plastic surgeon."
Film fantasies play a part in the choice of secret entrances. "Many of my clients come to me knowing what movie secret door they would like duplicated," says Humble, who cites as top inspirations Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade, the Batman and James Bond franchises, Mr. & Mrs. Smith and Goonies, on which a popular access control device that "requires that a certain sequence of notes be played on the piano to get the door to open" is based. There's also Get Smart: "At this moment, we are converting a phone booth [inside a private residence] so that when the user dials the correct number, the back panel opens to grant access to a secure area." He adds: "I can tell you that we've built secret doors for many of the most recognizable and highly awarded directors and celebrities in Hollywood. There are a lot of Oscars and Emmys tucked away safely behind my secret doors."

1. A floor plan for an $8.35 million, 6,000-square-foot bunker from Texas company Rising S Bunkers includes a decked-out game room.

2. The largest swimming pool that Rising S has built measures 40 feet.

3. Fitness rooms are a must to compensate for a lack of outside activity.

4. Natural light tubes and ultraviolet LED lamps promote growth in underground gardens of consumable plants and vegetables.

5. Theaters seat as many as 20 people and come with 10-foot screens.

6. Rising S has seen garages with 15 vehicles, including Rolls-Royces, muscule cars and armored personnel carriers (one client has three).