Deployment of Russia’s hyper-sonic missiles is causing heartburn in the West. Media headline the news as a dramatic breakthrough on a par with the first Sputnik. “Experts” are rushed into play like those self-styled pundits pronouncing when the initial exit polls appear on Election Day. Pentagon officials assure us that the United States is at the top of the nuclear game and able to respond to (if not exactly match) anything that the Russians can put out there.
Ninety eight percent of all this instant reaction is “fog-horning.” It simply signals that something big and important is out there even though we don’t have a clear picture of its actual shape or dimensions — or its significance. That’s normal. What counts is moving swiftly to the “searchlight” stage of close observation and hard thinking.
Whether analysts, official or otherwise, get there is problematic. We’re out of practice when it comes to serious strategic appraisal. After all, we’ve been flailing about in Afghanistan for almost two decades with no realistic aim or evaluation of the chances of achieving it by whatever means at whatever cost. The disorientation on Syria is even greater. There, we haven’t as much as figured out who are the “bad guys” and who are the “good guys” — except for ISIS.
If you can’t differentiate friend from foe for want of rigorous strategic analysis, your actions are predictably erratic — little more than the expression of mental fibrillations. The same can be said for the rest of the Missile East.
The Washington consensus is sure about one thing: Russia is a mortal enemy. We sanction the Russians, we denounce the Russia, we coerce our European partners into ostracizing them, we conjure frightful images of Vladimir Putin while ignoring just about everything he says (as if they were Hitlerian rants). Still, no one seems able to provide a crisp formulation of what the Russian threat is — other than getting in our way in places where we demand to have full sway: Syria, Libya, Iran, Turkey, Ukraine, Georgia.
Of course, we also accuse them of working relentlessly to undermine American democracy. Yet, that remains debatable as does everything that bears the dubious label of “Washington consensus.” Anyway, whatever minuscule role the Kremlin might have in the accelerated unravelling of the American Republic, it barely registers amidst the hammer blows struck by the craziness of President Donald Trump, his enablers and a largely compromised, abject resistance.
Cold War Dread
Understandably, it is not that easy to overlook nuclear weapons. It wasn’t that long ago that many of us were tormented by the dread of a prospective Armageddon, when the Cold War carried manifest dangers, when the air was thick with hostility and menace.
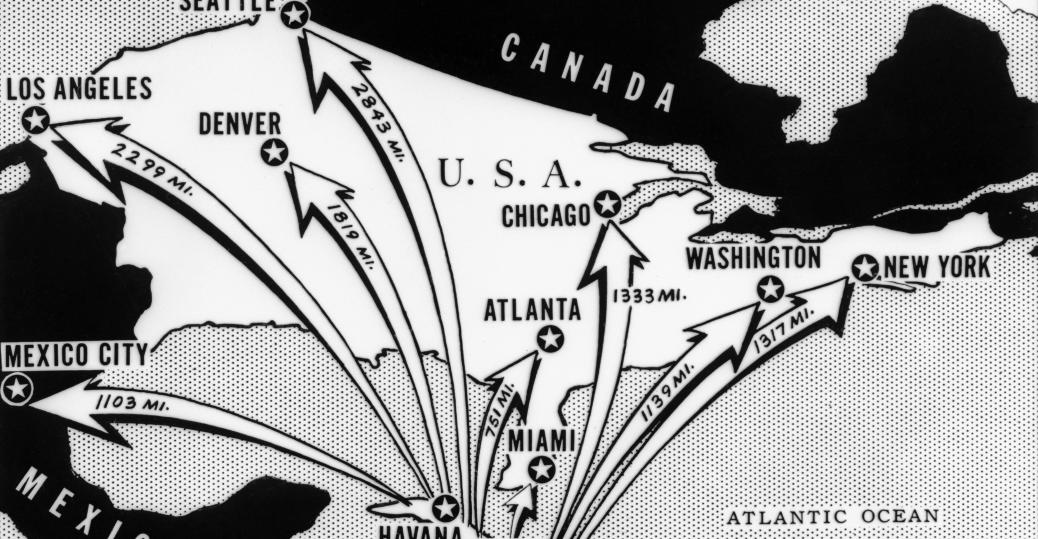
In October 1962, Americans were terrified over Soviet missiles in Cuba, as this newspaper map showing distances between Cuba and major North American cities demonstrates.
Those acute fears gradually faded over the 40 years of the nuclearized Cold War. We came to live with the Bomb — if not to love it. Subsequently, concerns shifted to the risks associated with nuclear weapons proliferation among less stable states in more fraught places.
The reasons for this sedating were three-fold.
- Above all was the “balance of terror.’’ Leaders among the major nuclear powers absorbed the fundamental truth that not only was the notion of “winning” a nuclear war an oxymoron — but also that any use of nuclear weapons inexorably would escalate into acts of collective suicide. The survivors would envy the dead — as Nikita Khrushchev one said. That conviction became formalized in the doctrine of Mutually Assured Destruction.
- Second, it was reified by a number of treaties and understandings: START I,II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty), the Anti-BallisticMissile Treaty (ABMT), the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, introduction of the Hot Line between the White House and the Kremlin, and the several arms reduction accords signed when Mikhail Gorbachev came to power in Moscow. Their collective purpose was to ensure that no conceivable advantage might be gained that would jeopardize — however slightly — the balance of nuclear power, i.e. the assurance that any resort to nuclear weapons was tantamount to the death of civilization.
- Finally, a number of technological developments reinforced Mutual Assured Destruction: the deployment of submarine launched ballistic missiles — SLBM (immune to location and possible destruction in a “first strike” — thereby, guaranteeing a retaliatory capability); improved controls that reduced the chances of an “accidental” or miscalculated launch; and the moratorium in placing ballistic missile defenses around major population centers that could have the effect of removing their “hostage” status.
The last has turned out to be a largely redundant measure since the strenuous efforts of the Pentagon/NASA as well as their Soviet/Russian counterparts to devise a workable BMD all have come up well short of producing anything meaningful.
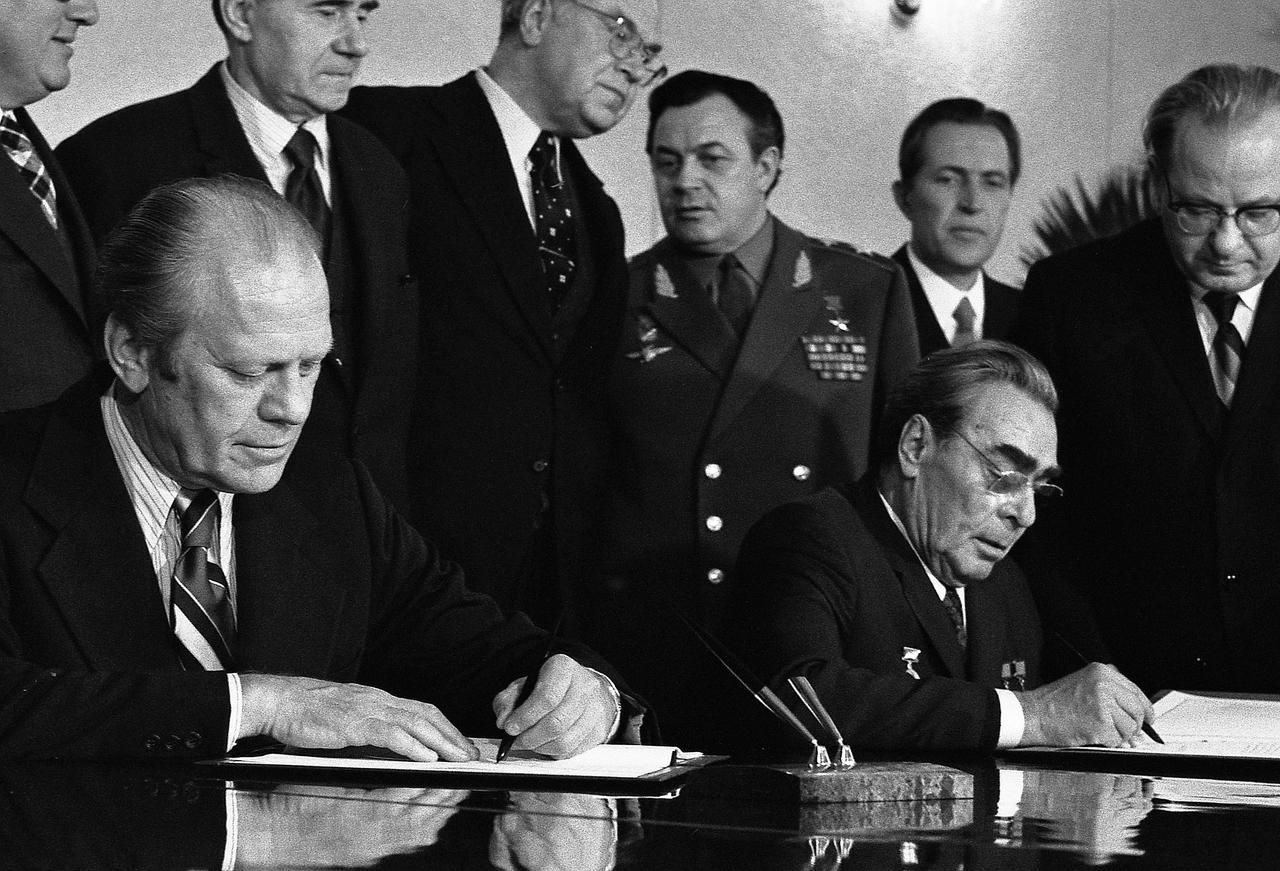
U.S. President Gerald Ford and Soviet Premier Leonid Brezhnev sign joint communiqué to limit strategic offensive arms, 1974. (Wikimedia)
Unfortunately, two policy developments have awakened the nuclear issue from its somnambulant state. One is Washington’s abandonment of arms control treaties that were important parts of the nuclear stability package. George Bush removed us from the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty(while observing its provisions), and effectively voided restrictions on ballistic missile defense in the vain hope of countering remote threats from prospective nuclear powers (Iran), bolstering the sense of security of some East Europeans (a non-solution to a non-problem)and – frankly – to get under the Russians’ skin. Barack Obama had neither the conviction nor political courage to reverse those retrograde moves.
Under Donald Trump, there has been a comprehensive plan to break free of all manner of restrictive commitments — military, diplomatic or economic. Deployment of regional BMD systems directed at Russian, Chinese and North Korean forces has been expanded despite their demonstrated efficiencies (one version could not even protect Saudi oil complexes or U.S. air bases in Iraq from primitive Iranian missiles).
Modernization of Nuclear Arsenals
The other troubling development concerns the modernization of nuclear arsenals by both the United States and Russia. President Barack Obama committed us to a trillion-dollar program to refine and upgrade American warheads and delivery systems over the next 20 years. The strategic rationale is obscure.
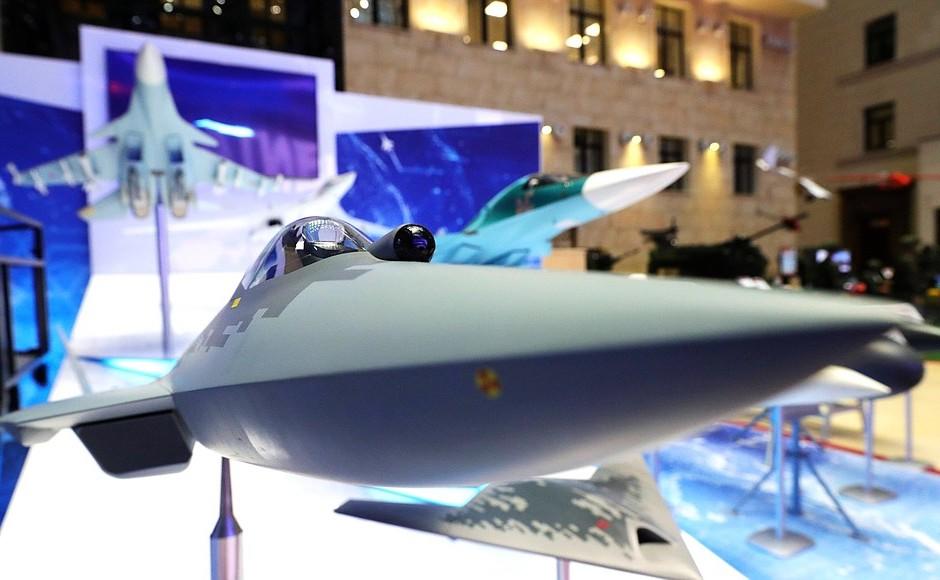
The Russian hypersonic missile development is a parallel development. In a purely technical sense, they obviously are “ahead” of us. And that irritates the hell out of the American security establishment.
Does being “ahead” have any practical meaning, however? Is there a genuine contest for advantage that translates into their gaining an upper hand in some sense or other? The clear answer is “NO!” It is strategically meaningless. Why? Because it in no way alters the logic of Mutual Assured Destruction.
Theoretically, there are only two imaginable ways to do that. The most significant would be development/deployment of a massive, truly effective BMD system that shields population centers and other critical, high value sites from retaliatory attack. That has shown itself to be impossible – even if the initiator of an attack succeeded in reducing the other side’s retaliatory forces by some significant fraction.
A totally disarming first strike in principle could be the second method logically to qualify MAD. It cannot be done, though.Fortunately. The combination of SLBMs, cruise missiles, and increased warhead lethality makes the idea of a disarming first strike a pipe dream of military strategists disengaged from reality. Hypersonic weapons do not change that calculus.
Accuracies of MIRVed warheads were lowered to 100 feet many years ago.(CEP, or Circular Error Probability = 50 percent chance of landing within radius.) Reducing that to 20 feet, therefore, is pointless – the silo is destroyed either way unless its missile has been “launched on warning” (tripwire automaticity as ultimate assurance of retaliatory strike). Similarly for missile defense.
Then, there is the question of an incoming missile’s speed. Current ICBMs that may give 18 minutes warning do not permit any defensive measures to be taken. If they arrive on target within six minutes, there is no additional benefit to the attacker. Today’s missiles that follow a straight trajectory cannot be intercepted — with or without their distracting decoys.
The fact that “swerve” capable hypersonic missiles can mambo their way to the target adds nothing to their effectiveness. Anyone who tells you that the Russians gain a strategic advantage thereby is lying — either in order to extract larger sums for R & D from the Treasury or to accentuate irrational fears of Russia.
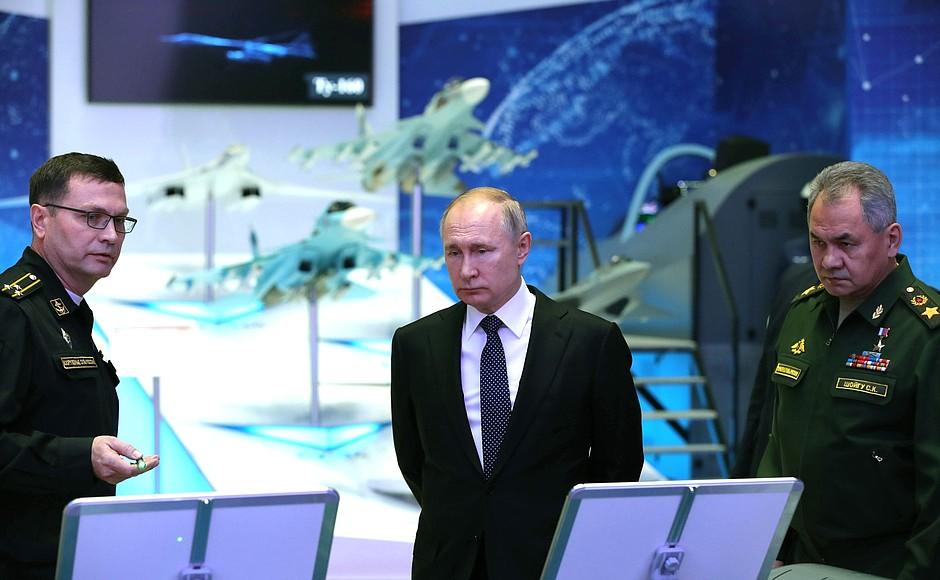
President Vladimir Put visiting an exhibit of advanced weapons before meeting with Russia’s Defence Ministry Board, December 2019. (The Kremlin)
Finally, no reasonably sane leader would risk national suicide for a 1 percent chance of getting away with a first strike and surviving retaliation. There is no stake worth even contemplating it. Indeed, that logic holds even were there an impossible 50 percent chance of pulling it off.
Today, the United States and Russia are not engaged in a life-or-death struggle for world domination or for ideological vindication. Ascribing anything like that notion to Vladimir Putin is simply a sign of mental derangement – ours, not his. The same holds for the super-power competition between the United States and China.
So, if this line of reasoning is compelling, why did Russia’s leaders bother with investment of great sums to produce hyper-sonic missiles? The answer is a matter of speculation. Doubtless, technological and bureaucratic momentum has much to do with it. These sorts of long-term programs take on a life of their own — just as they do in Washington. The is no more reason for the United States to squander a trillion dollars in refining our nuclear arsenal as two successive administrations have committed us to doing.
In Russia’s case, there likely is another factor at work. Historically, Moscow leaders have exaggerated American technical capabilities; they have something of an inferiority complex on this score despite their own remarkable accomplishments. It is particularly acute in the nuclear realm — most especially in regard to ballistic missile defense.
This goes back to Nixon’s proposed Safeguard system, followed two decades later by Reagan’s Star War’s plans. Neither of which in actuality had the potential to alter the strategic balance. This free-floating strategic anxiety should be placed in historical perspective. There is a touch of paranoia in the Russian strategic mind — engraved by the events of the 20th century.
Some of this sentiment is conveyed by Putin’s remarks in announcing the deployment of hypersonic missiles: “We’re used to being in the position of catching up. That no longer is the case. Russia is the only country that has hypersonic weapons.”
To some unknowable degree these neuralgic points in the Russian psyche have been stimulated by the aggressive American program to surround Russia with BMD systems. “Might it just be conceivable that the United States could perfect them, make it work, and somehow jeopardize the credibility of our nuclear deterrent? Why are they expending so much money and effort? Why do those BMD sites make Poland and the Baltics feel more secure when they are in fact militarily useless and it makes no sense for us to attack them?”
Informed analysis suggests that the answer is negative to all these questions. The alternative explanation: U.S. leaders are inclined to do feckless things; they are strategically obtuse.
The broader lesson is that there is truth to the old adage: “Russia never is as strong as it seems; Russia is never as weak as it seems.” We wrote it off as a world power in the 1990s and never since made the proper adjustment. That perception may have contributed to the glaring failure of the United States’ intelligence community in missing Russia’s remarkable break-throughs in weaponry.
It’s intelligence that counts more than Intelligence.