When it comes to estimating the human capital and potential fallout from a highly contagious epidemic, arguably the most important variable is the R0 ("R-naught") value of the disease, which represents the average number of secondary cases arising from an average primary case in a entirely susceptible population. That's the technical definition, a simpler one is that the R0, or basic reproductive number, of a contagious disease is the number of cases that a case of the disease generates over the course of its infectious period in a susceptible population. The higher this number, the more dangerous the disease, the more lethal the outcome.
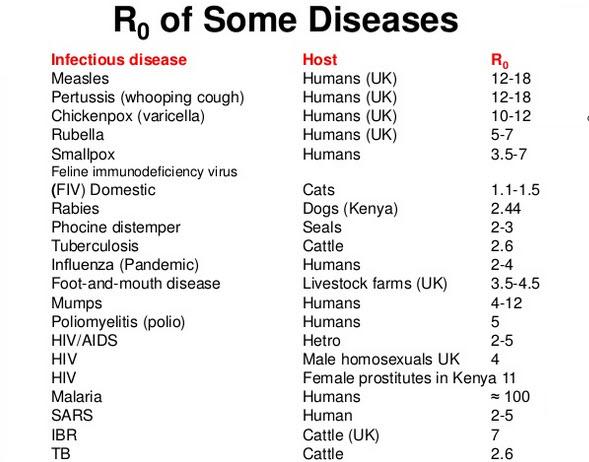
Some indicative R0s are 0.9 – 2.1 for the common flu while the 1918-1919 pandemic-causing Spanish flu was estimated to have ranged from 1.4 – 2.8, with a mean of 2. Some other notable R0s are shown below, and note that SARS was between 2 and 5:
So what about the R0 of 2019-nCoV, also known as the coronavirus that has claimed over three dozen lives in China and infected (at least) 1,000 people? Naturally, since the disease is most active in China which is notoriously opaque especially when it comes to matters that can cause a mass panic, the best one can do is guess, and that's what the World Health Organization did yesterday when it issued a statement on the coronavirus epidemic with the following projection:
Human-to-human transmission is occurring and a preliminary R0 estimate of 1.4-2.5 was presented. Amplification has occurred in one health care facility. Of confirmed cases, 25% are reported to be severe. The source is still unknown (most likely an animal reservoir) and the extent of human-to-human transmission is still not clear.
Needless to say, while 2.5 is quite high, and in line with that of the Spanish flu epidemic which infected about half a billion people back in 1918, killing as many as 100 million before it eventually fizzled out, the real coronavirus R0 number may end up being far higher. That is the working hypothesis of Jonathan Read, a UK expert on the transmission and evolutionary dynamics of infectious diseases, who has published a paper with four colleagues that estimates transmission parameters for the Wuhan coronavirus, calculates that the R0 of 2019-nCoV to be between 3.6-4.0 or roughly the same as SARS, and reaches a conclusion about spread of the coronavirus epidemic that is frankly terrifying.
In "Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic predictions", Reed et al, write that with an R0 of between 3.6 and 4.0, roughly 72-75% of transmissions "must be prevented by control measures for infections to stop increasing."
This is a major problem because Reed estimates that only 5.1% of infections in Wuhan are identified (as of Jan 24), "indicating a large number of infections in the community, and also reflecting the difficulty in detecting cases of this new disease." Furthermore, since all of this is happening in China which is not known for making the most socially-beneficial decisions under pressure, there is an ominous possibility that Reed is actually overly optimistic.
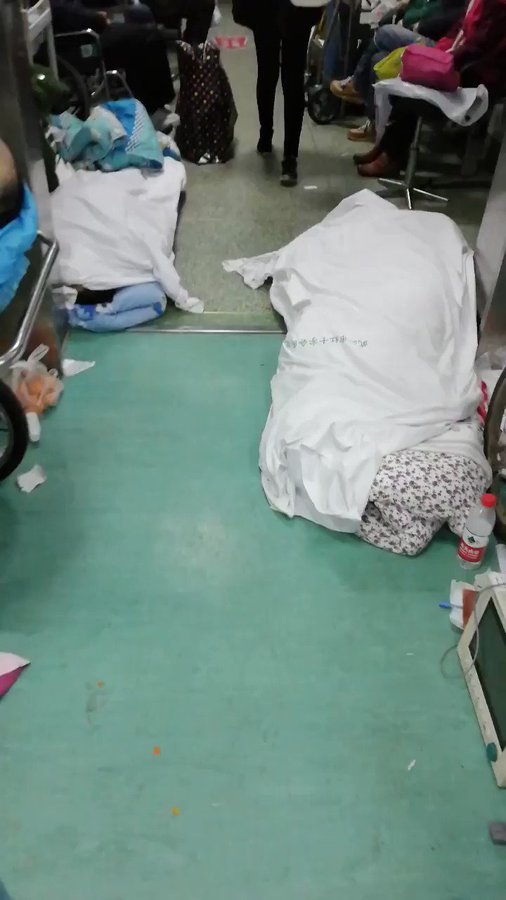
Huge public hygiene crisis seems to have erupted in #Wuhan. This video clip was once posted on Weibo but now deleted. The lady in the clip says dead bodies were left at hospital aisles untreated whereas doctors are taking care of other patients alongside them. #WuhanPneumonia
2,623 people are talking about this
Reed wastes no time to get to his terrifying conclusion which is that if no change in control or transmission happens, then further outbreaks will occur in other Chinese cities, "and that infections will continue to be exported to international destinations at an increasing rate."
As a result, in 10 days time, or by February 4, 2020, Reed's model predicts the number of infected people in Wuhan to be greater than 250 thousand (with an prediction interval, 164,602 to 351,396);
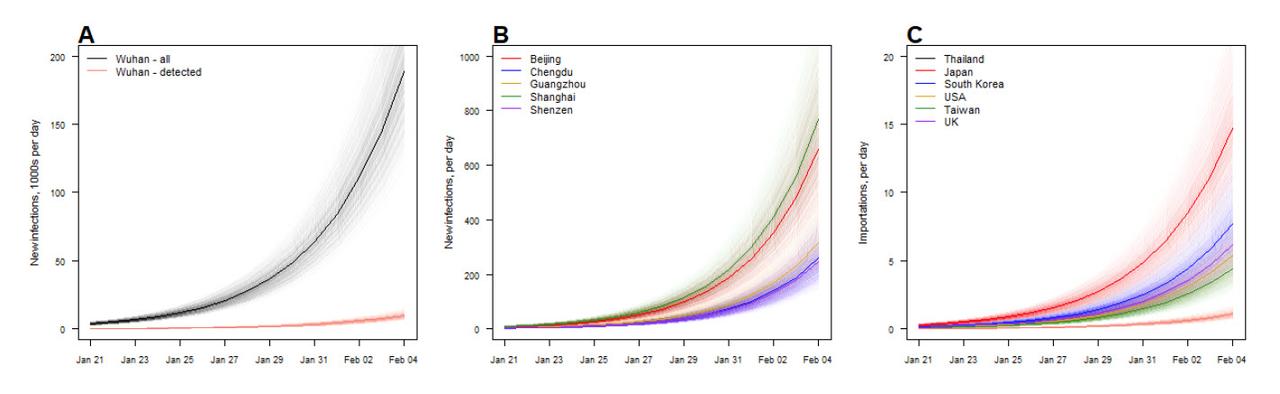
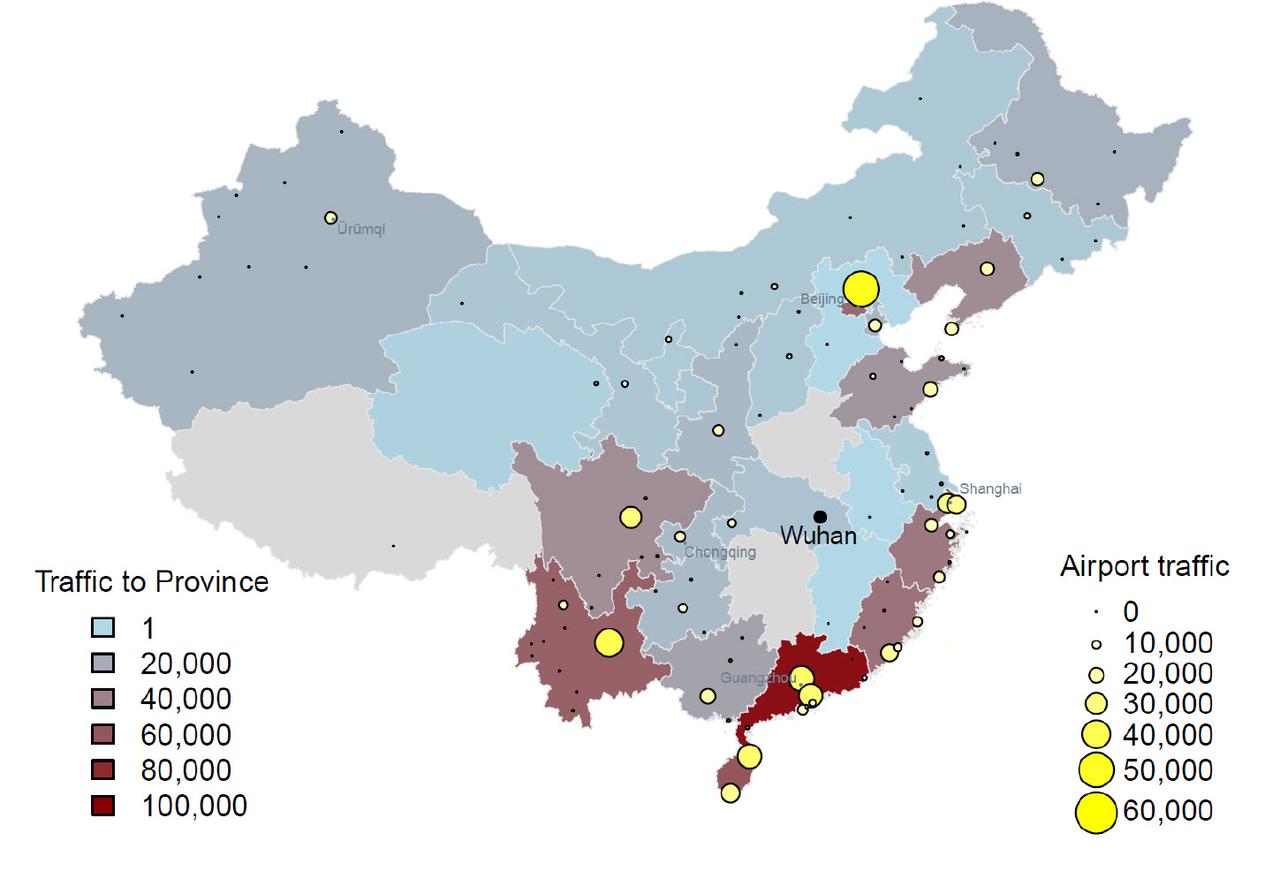
After Wuhan, the cities with the largest outbreaks elsewhere in China are expected to be Shanghai, Beijing, Guangzhou, Chongqing and Chengdu.
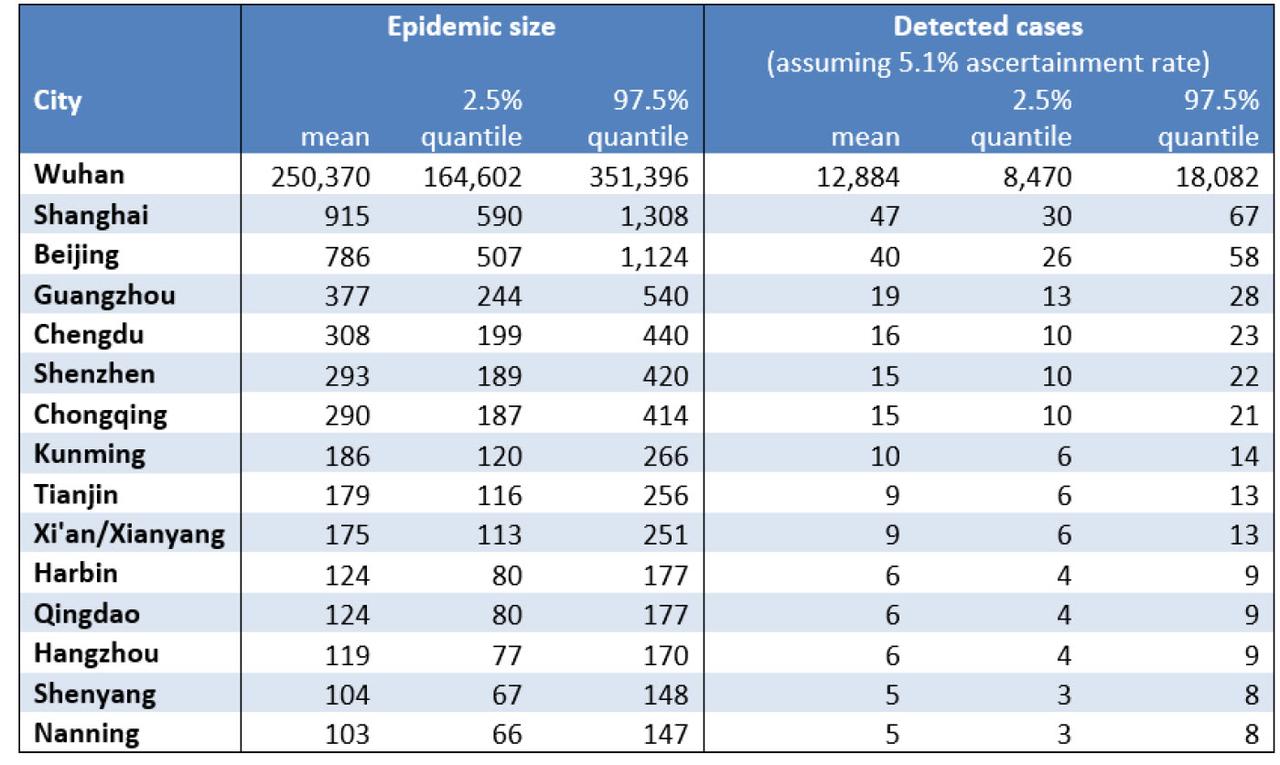
Reed also predicts that by 4 Feb 2020, the countries at greatest risk of importing infections through air travel are Thailand, Japan, Taiwan, Hong Kong, South Korea, USA, Malaysia, Singapore, Australia and Vietnam. In short: much of Asia will infected, and from there, the rest of the world awaits.
Critically, Reed's model alleges that Beijing was woefully late in its response and that recently imposed "travel restrictions from and to Wuhan city are unlikely to be effective in halting transmission across China; with a 99% effective reduction in travel, the size of the epidemic outside of Wuhan may only be reduced by 24.9% on 4 February."
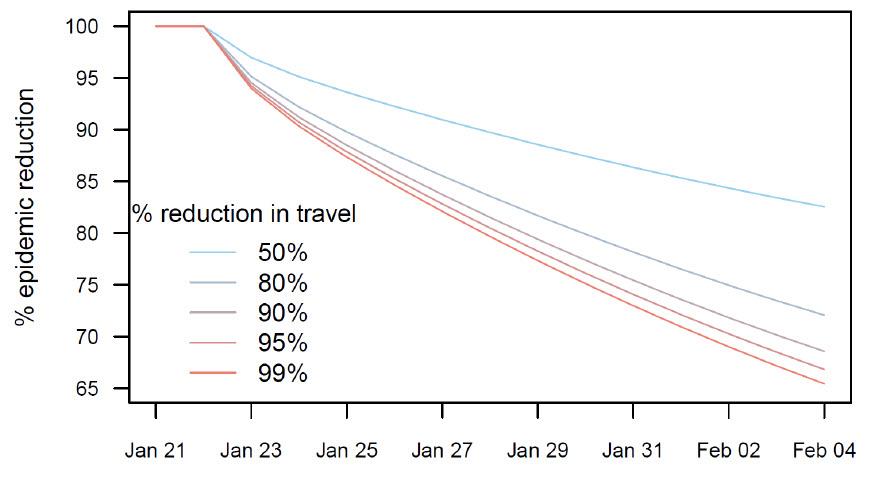
Reed's prediction is in line with other modelling studies of travel restrictions, which find that reducing travel only serves to delay the epidemic reaching other locations, rather than suppressing the spread entirely. Still, it is important to note that his model only considered air travel, and did not consider the potential impact of travel restrictions relating to land transportation.
That said, Reed admits there is a chance that he is wrong, largely due to using flawed assumptions:
Our findings are critically dependent on the assumptions underpinning our model, and the timing and reporting of confirmed cases, and there is considerable uncertainty associated with the outbreak at this early stage.
Yet even with these caveats in mind, Reed's work suggests that a basic reproductive number for this 2019-nCoV outbreak is materially, perhaps catastrophically higher compared to other emergent coronaviruses, "suggesting that containment or control of this pathogen may be substantially more difficult."
Even assuming that most of Reed's assumptions are overly harsh and pessimistic, his summary leaves little hope that the Coronavirus epidemic will be contained any time soon:
"We are still in the early days of this outbreak and there is much uncertainty in both the scale of the outbreak, as well as key epidemiological information regarding transmission. However, the rapidity of the growth of cases since the recognition of the outbreak is much greater than that observed in outbreaks of either SARS or MERS-CoV. This is consistent with our higher estimates of the reproductive number for this outbreak compared to these other emergent coronaviruses, suggesting that containment or control of this pathogen may be substantially more difficult."
Finally, while Reed makes no observations on the potential mortality associated with nCoV, one can make a broad observation: late on Friday, China's Hubei province reported 15 additional coronavirus deaths, which added to the previously reported 26 casualties, bringing the total to 41. And with roughly 1,100 confirmed cases, this means that the mortality rate of the diseases has just jumped from roughly 2.5% to 4%. Which means that if Reed is correct, and if 250,000 people in Hubei alone will be infected by February 4, no less than 10,000 Chinese people will be dead in the next 2-3 weeks.
What happens after that - with China effectively paralyzed by fear and the economy grinding to a halt as nobody leave their home - is anyone's guess.